Importance
The expansion and management of airport infrastructure have led to an increase in energy consumption. As electricity generation often involves greenhouse gas emissions, this contributes to climate change. Therefore, Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) is committed to playing a role in helping to limit the rise in global average temperature by transitioning from traditional fossil fuel energy to clean energy, alongside implementing efficient energy management practices.
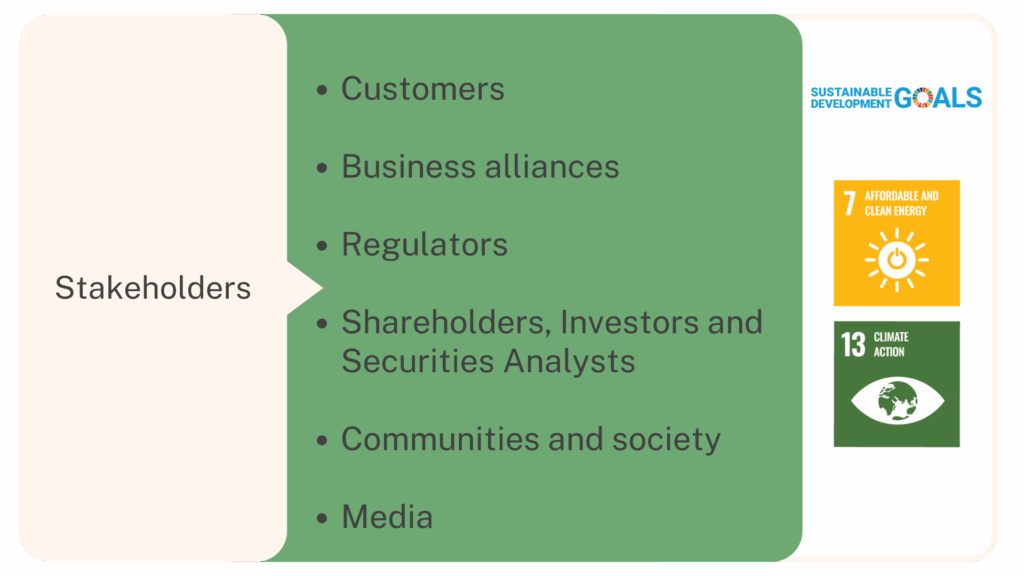
This approach aims to mitigate indirect environmental and social impacts, while also responding to the expectations of various stakeholders, including shareholders, investors, analysts, and regulators who are increasingly focused on sustainable investments and global sustainability standards. Additionally, there is a growing number of environmentally conscious customers each year.
If AOT can effectively identify climate-related opportunities and manage associated risks in accordance with international standards, the company will not only enhance its corporate image and actively contribute to climate change mitigation, but also attract global investors and environmentally conscious customers — ultimately supporting long-term business sustainability.
Policy
AOT’s Commitment

Policy, Action Plan, and Related Practices
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) is committed to managing all airports under its responsibility in alignment with sound environmental practices, with the ultimate goal of transforming all six airports into internationally recognized Low-Carbon Airports. The company’s efforts are guided by the framework of the Airport Carbon Accreditation (ACA) program, initiated by the Airports Council International (ACI).
To ensure concrete implementation, AOT has established the Sub-Committee on Sustainable Development and Climate Change under the Board of Directors (Board Oversight) to drive relevant policies and action plans forward. This sub-committee is also tasked with closely monitoring the progress and performance of all departments to ensure alignment with AOT’s environmental policy, including key programs related to climate initiatives, such as climate lobbying activities conducted through contributions to trade associations and policy–focused initiative.
Furthermore, AOT’s environmental management initiatives at all six airports are carried out in accordance with the AOT Corporate Plan for Fiscal Years 2023 – 2027 (Reviewed for FY2024). These efforts fall under the Airport Strategic Positioning framework and the company’s Environmental Policy for Airports, reinforcing a unified and compliant approach to environmental governance—strictly adhering to all applicable laws and regulations.
Recognizing the urgency and importance of energy management and climate change mitigation, Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) has established relevant policies, action plans, and operational guidelines, which include the following:
Climate Policy and Activities of the Trade Association – Airports Council International (ACI)

Airports Council International (ACI) plays a significant role in mitigating the impacts of climate change through its environmental initiative, the Airport Carbon Accreditation (ACA) program. This program encourages airports to reduce CO₂ emissions in order to achieve various levels of carbon accreditation. In addition, ACI promotes long-term capacity building among its members, such as the adoption of clean technologies, the reduction of carbon and greenhouse gas emissions, and the pursuit of new market opportunities.
AOT has formulated and disclosed related policies to support and monitor its environmental performance. This is achieved through internal collaboration among international affairs and environmental management departments, under the Management System for Lobbying Activities and Trade Association Memberships. AOT maintains a firm stance in supporting external organizations and policies that are aligned with the Paris Agreement.
AOT’s scope of support for the ACA program includes the following key actions:
- Supporting airports in reducing carbon emissions as a response to climate change
- Promoting the adoption of clean technologies at airports to reduce pollution
- Setting long-term targets for carbon reduction with consideration of climate change impacts
- Focusing on adaptation and enhancing climate resilience
Should ACI revise its position on climate change in the future, AOT will undertake a review of its support approach to ensure alignment with the updated direction, in line with the Paris Agreement Review and Monitoring Process.
In support of climate change mitigation aligned with the Paris Agreement, Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) has engaged in knowledge exchange on airport operations and cultivated strategic relationships with executives from airports in other regions. These efforts have enhanced market and trade opportunities through business alliances and trade associations, while also strengthening AOT’s reputation as a leader in air cargo transportation—particularly in addressing climate change under the Net Zero agenda.
AOT’s membership in climate-focused associations further reflects its proactive role in supporting international policies and initiatives to mitigate the impacts of climate change through climate-related direct lobbying activities.
A notable example of AOT’s leadership in this area includes hosting the 18th and 19th ACI Asia-Pacific & Middle East Regional Environmental Committee Meetings on 12 – 13 March 2024 in Bangalore, Republic of India, and 10 – 12 September 2024 at the Chatrium Grand Bangkok Hotel, respectively.
In the event that the practices or positions of any association significantly conflict with AOT’s corporate stance, the company is prepared to express its views in a constructive and conciliatory manner, in line with its Framework for Addressing Misalignments.
Management Approach
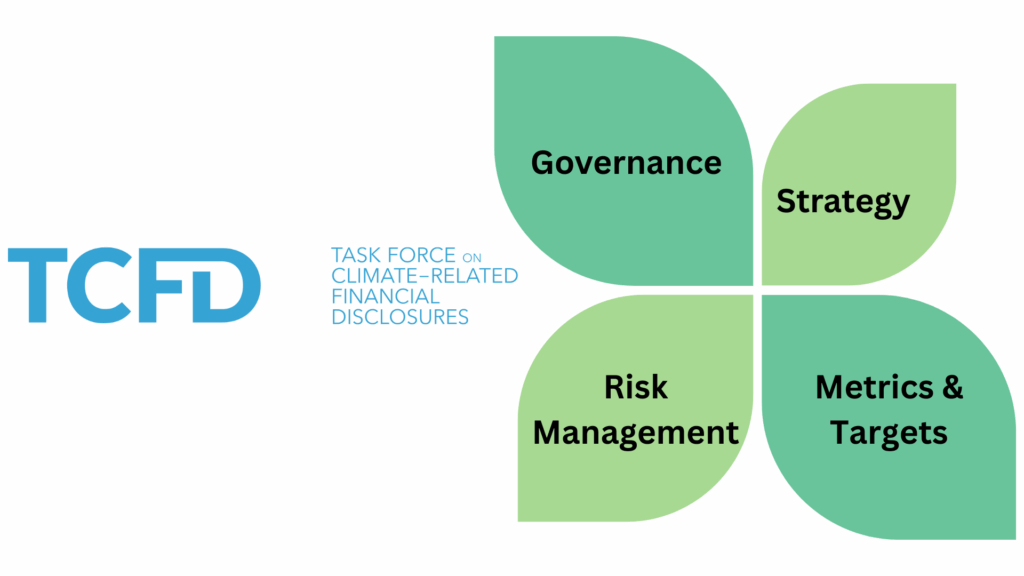
AOT has established an overarching environmental strategy and operational plans related to energy management and climate change, ensuring alignment with the framework of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). The strategy is structured around the following key components:
Overall environmental strategy
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD)
Governance
Climate Governance Structure
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) has established a clear governance structure for energy and climate change management, spanning from the Board Oversight level to operational management.
AOT has appointed the Board-Level Committee on Sustainable Development and Climate Change, which is responsible for overseeing climate-related issues. This committee comprises representatives from the Engineering and Construction Group and the Operations and Maintenance Group. The committee holds meetings at least annually to discuss progress in addressing climate change issue. The Corporate Strategy Department serves as a coordinating body to ensure that energy and climate-related initiatives align with international sustainability frameworks and assessment standards.
| Climate Governance Structure | Roles and Responsibilities | |
|---|---|---|
| Board Level |
|
|
| Management Level |
|
|
| Operational Level | Head Office | |
|
|
|
| Airports | ||
|
|
|
Incentives for Climate-Related Management
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) has established employee incentive mechanisms to enhance motivation and engagement in energy management and climate change initiatives. These incentives are structured into three levels as follows:
| President | Achievement of energy and climate change goals |
| Senior Management | Achievement of targets, measurement, and evaluation of eco-efficiency performance |
| Operational-level staff | Awards for Winners of the Innolution Creative Concept Project Competition |
Strategy
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) has established four key strategic approaches for energy management (Actions to Reduce the Amount of Energy Used) and climate change mitigation, as follows:
| ⚡ Energy Index | 🌍 Airport Carbon Accreditation (ACA) | 🤝 Collaboration with International Organizations | 🎯 Incentives for Climate-Related Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| AOT conducts annual energy audits and eco-efficiency performance assessments, covering its Head Office and all six airports under its operation. These assessments are based on data compiled from airport energy usage reports (Energy Reports), benchmarked against AOT’s revenue to evaluate energy performance in relation to economic output. In addition to collecting energy consumption statistics, AOT also conducts ongoing studies to identify new opportunities for reducing energy use. A dedicated budget has been allocated to support the implementation of these initiatives. | AOT collects and reports greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions data from all six airports under its operation, in accordance with the guidelines of the Airport Carbon Accreditation (ACA) program. Currently, five airports have sufficient data to be certified at Level 3 – Optimization, while one airport meets the requirements for Level 1 – Mapping. These certifications reflect the airports’ capabilities in data collection and implementation of GHG emission reduction measures across the supply chain, demonstrating an evaluation of progress in reducing energy consumption. All AOT airports have developed and implemented a Carbon Management Plan to support ongoing decarbonization efforts. |
|
AOT has established an incentive structure for its employees to enhance motivation in implementing energy and climate-related initiatives. The incentives are categorized into three levels:
|
Energy and Climate Risk Management Approach
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) has established an energy and climate risk management approach in alignment with its Risk Management Manual for Fiscal Year 2024. This approach is integrated throughout AOT’s business operations across the entire supply chain, both current and future business.
The process begins with climate scenario analysis, followed by risk and opportunity assessment, and continues through to the development of adaptation measures for physical climate risks.
A practical example of this integration is reflected in the design of AOT’s taxiways, which incorporate low-carbon service concepts. These taxiways are designed to minimize aircraft taxiing time from landing to terminal buildings, while maintaining compliance with safety standards set by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). This optimization helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions from airline operations.
|
🔍
3.1 Climate-Related Scenario Analysis
AOT conducts climate scenario analysis to forecast potential outcomes under various global temperature rise pathways, including scenarios where the average global temperature increases by more than, less than, or equal to 2°C (2°C or below, and above 2°C). The analysis covers both physical scenarios and transition scenarios to assess the potential climate-related risks and impacts on the organization.
|
📈
3.2 Financial Risk & Opportunities of Climate Change
AOT has identified short-, medium-, and long-term climate-related risks across its entire value chain (Time Horizon). This assessment encompasses both current and emerging climate-related factors, including:
In addition, AOT actively explores business opportunities arising from climate change, utilizing the Internal Carbon Price reference adopted from Singapore. This mechanism is used to drive internal behavioral change, enhance energy efficiency, and accelerate low-carbon investments across AOT’s operations. |
🔄
3.3 Climate Risk Adaptation
AOT has established a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) as a framework to address natural disaster risks resulting from climate change. The BCP is certified under the international standard ISO 22301:2019 for Business Continuity Management of Airport Services, covering both the Head Office and all six AOT-operated airports.
This certification is valid for a period of three years, from Fiscal Year 2022 to 2025 (FY2022–FY2025). The adaptation measures outlined in the BCP also extend to AOT’s future operational sites, ensuring climate resilience across its entire infrastructure. |
Climate Risk Assessment
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) has conducted a climate risk assessment for its six airports and Head Office, taking into account a comprehensive range of risks—including strategic, operational, financial, and regulatory risks.
The assessment revealed that climate change has increased both the severity and likelihood of natural disasters, which are considered overall risk factors affecting AOT’s operations and finances. These are classified as physical risks under the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework.
The findings indicate that climate-related disasters pose moderate risks (with low severity but an annual likelihood), particularly in terms of operational risk and financial risk. If a disaster occurs, it could damage aircraft, ground vehicles, and service equipment; disrupt ground and air transportation; and result in injuries or fatalities to passengers and staff, as well as damage to property and revenue loss.
The projected impact is equivalent to up to one-quarter of operations and services being disrupted for no more than one hour per incident, with an estimated occurrence frequency of once per year. The affected resources include:
- Personnel
- Buildings and facilities
- Equipment and tools
- Utilities and infrastructure
- Transportation
- Financial resources
- Business partners, service providers, and other stakeholders
To address these risks, AOT has established disaster response strategies for climate-induced events and has integrated these measures into its Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to enhance organizational resilience.
Example: Climate Risk Assessment – Don Mueang International Airport
| Climate Change Risk: Natural Disasters | Risk Level | Management Approach | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Management | Target | After Management | ||
| Flood | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Establish a rainwater management plan, implement external flood barrier systems, and maintain and repair the drainage system. |
| Storm | Moderate | Low | Low | Install weather alert systems and establish close coordination protocols with the Meteorological Department and Aeronautical Radio of Thailand. |
| Fire | Moderate | Low | Low | Establish operational procedures in the event of a fire. |
| Earthquake | Moderate | Low | Low | Install a power outage prevention system in response to earthquakes. |
Metrics & Targets
| Target | Unit | Base Year | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tons of carbon dioxide equivalent per passenger | Base Year | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% |
| Achieve a 20% increase in carbon dioxide absorption from the base year (2024) by the year 2028. | CO₂e | Base Year | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% |
Remarks:
- The base year values and target figures are subject to revision upon finalization of the base year data. Relevant internal departments may be requested to collaborate on a project-by-project basis, as appropriate.
- Targets 1 and 4 are currently under study and being incorporated into the Environmental Master Plan. Once concrete action plans are in place, the targets will be recalculated and reviewed accordingly.
Airport Carbon Accreditation (ACA)
AOT controls greenhouse gas emissions from airport operations in alignment with the Airport Carbon Accreditation (ACA) framework. Greenhouse gas emissions data are collected and reported for all six AOT-managed airports. These airports are accredited at Level 1 (Mapping), which involves carbon footprint data collection, and Level 3 (Optimization), which involves collaborative carbon footprint reduction across the supply chain.











Note:
- Level 1 (Mapping): Preparation and third-party verification of a carbon footprint report for airport operations in accordance with the ACA standard.
- Level 2 (Reduction): Development of a Carbon Management Plan that outlines emission reduction targets and implementation strategies.
- Level 3 (Optimization): Expansion of the carbon footprint reporting boundary to include emissions from the broader airport supply chain.
- Level 4 (Neutrality): Achievement of carbon neutrality through the purchase of carbon credits to offset the airport’s remaining greenhouse gas emissions.
Performance
Energy Performance
ICT as a Low-Carbon Enabler
In alignment with global technological trends, AOT has adapted and reinforced its commitment to integrating environmentally friendly information and communication technologies (ICT) into its operations in a systematic and comprehensive manner. This includes reducing energy consumption and optimizing the use of ICT resources to ensure efficient service delivery without compromising quality. AOT aims to promote sustainable business growth through the implementation of the AOT Green ICT Management Policy, which governs the selection and use of environmentally friendly ICT solutions.
Energy Conservation Projects at 6 Airports (AOT Electricity Consumption Reduction Program)
AOT has implemented energy conservation projects across its six airports, setting annual targets to reduce electricity consumption compared to the previous year’s usage. Each airport under AOT’s management is required to conduct activities throughout the fiscal year to achieve these targets. Key initiatives include replacing traditional lighting with energy-efficient LED systems, enhancing the efficiency of chiller systems, and providing training to raise awareness among AOT employees on the environmental and social impacts of electricity consumption. The training also emphasizes the benefits of improving energy efficiency and transitioning to clean energy sources.
Additionally, all six airports are required to submit annual reports detailing electricity usage and related expenditures. These reports serve as AOT’s internal audit mechanism to identify opportunities for improved energy efficiency and further electricity reduction in future operations. The table below summarizes the performance results of the Energy Conservation Project across the six airports for the year 2024 (FY2567).
| Airport | Electricity Reduction Target (Compared to 2023) | Performance Results for 2024 | Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suvarnabhumi Airport | A reduction of 0.39% | A reduction of 0.39% |
|
| Don Mueang International Airport | A reduction of 0.2% | A reduction of 1.24% |
|
| Chiang Mai International Airport | A reduction of 1% | A reduction of 3.18% |
|
| Phuket International Airport | A reduction of 0.06% | A reduction of 0.06% |
|
| Hat Yai International Airport | A reduction of 1% | A reduction of 1.41% |
|
| Mae Fah Luang – Chiang Rai International Airport | A reduction of 1% | A reduction of 0.89% |
|
Establishment of Internal Carbon Pricing for Assessing Financial Impacts of Transition Risk: Climate Regulation (Carbon Tax)
The use of an internal carbon price (ICP) is considered a regulatory mechanism aimed at reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions under the Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) framework. This may lead to the future implementation of a carbon tax in Thailand. AOT has adopted an internal carbon price based on Singapore’s carbon tax rate—the first in Southeast Asia to enforce such regulation. The benchmark carbon tax rate used is 5 SGD/tCO₂e (approximately 115 THB/tCO₂e), which serves as a reference within the organization. This internal pricing supports executive decision-making regarding energy performance improvements and carbon reduction-related project investments.
Energy Conservation Behavioral Initiative
“Car Free Day:
Let’s walk, cycling or use public transportation to reduce the use of personal cars and promote environment-friendly alternatives. Together, we can create meaningful change and make our city a better place.”
“Eco-Friendly Tourism: 6 ideas for Eco-Friendly Travel AOT encourages all passengers to travel together with Low Carbon Tourism.”
Climate Action Highlights
Thailand’s First Model Green Airport
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) is committed to advancing Suvarnabhumi Airport as the first Green Airport model in Thailand. This initiative emphasizes continuous improvement in environmental and energy management.
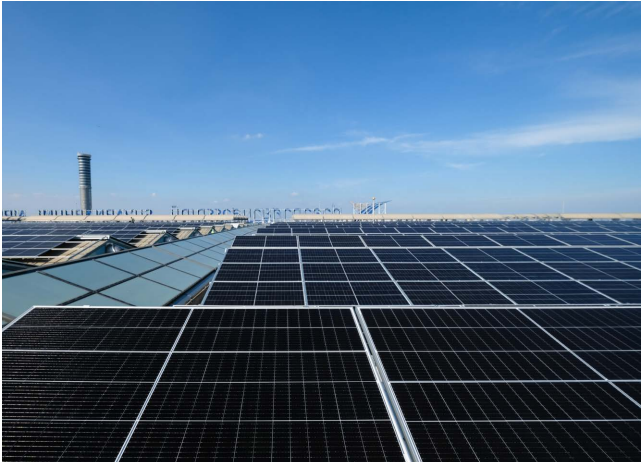
The new SAT-1 terminal has been designed as a Sustainable Building, integrating both Solar Rooftop and Floating Solar Power Systems. These renewable energy installations generate more than 78,000,000 kWh per year, helping avoid 7,277.82 tCO₂e annually.
In addition, the SAT-1 terminal was awarded the prestigious Prix Versailles under The World’s Most Beautiful List 2024 in the Airports category by the Prix Versailles Selection Committee, in collaboration with the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).

| ☀️ Solar Rooftop on Passenger Terminal |
☀️ Solar Rooftop on AMF Building |
☀️ Solar Rooftop & Floating Phase 2 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Design of the 3rd and 4th Runways to Reduce Aircraft Fuel Consumption
Airports of Thailand (AOT) has implemented the commissioning of the 3rd Runway at Suvarnabhumi Airport, which officially commenced operations on November 1, 2024. In addition to enhancing service efficiency and expanding business growth opportunities by increasing the airport’s capacity from 68 to 94 aircraft movements per hour, the runway was designed to shorten aircraft taxiing, departure, and landing times. This contributes significantly to reducing aircraft fuel consumption and is associated with engine emissions. Furthermore, AOT’s runway design adheres strictly to the safety standards of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).

Note: Calculations are based on the Emission Factor from the Airport Carbon and Emission Reporting Tool (ACERT) version 4.1, developed by ACI. The referenced values are as follows:
- Emission Factor: 3.1528 kgCO₂e per kg of fuel
- Fuel savings per flight: 0.012 tons/flight
- Emission Factor equivalent: 3.1528 tons CO₂e per ton of fuel
Energy-Efficient Buildings with LEED Gold Certification
AOT has undertaken the construction of its second Headquarters Building and the Institute of Airport Studies Office Building with a focus on high-performance and environmentally conscious design. The buildings are designed to optimize resource and energy use, promote environmental sustainability, and enhance the quality of life for occupants.
Both buildings fall under the LEED for Building Design and Construction (LEED BD+C) category, which applies to new constructions or major renovations. AOT is pursuing LEED Gold Certification for both buildings, reflecting its commitment to energy efficiency and sustainable building practice
Environmental Lectures and Engagement with External Agencies









